PROFESSIONAL OPTICS
AN INVESTMENT IN FAMILY
LEARNING THAT WILL LAST A
LIFETIME
This Telescope tube assembly is the match for the German Equitorial Mount feathured below. This is a 9.25" Schmidt-Cassegrain Optical Reflector Tube that is high quality and will last a lifetime.
You must look at this as an investment in a hobby for the whole family. Amazon.com is presenting this telescope at an amazing price of: $ 1,432.56 and that is a real bargain. The hobby of Astronomy will astound you and your family. Purchase of a quality instrument will be an investment in you and your childrens future. Astrophotography is an astounding and facinating hobby. Trips to the mountains and desert as camping and astronomy adventures will be remembered for a lifetime. The bonds created by the experiences and interactive moments will be very rewarding and always charished.
To check out the offer at Amazon.com, please click on the image above. By clicking "Read more" below, you can read technical information and specifications. Images taken from this scope are included in the series of information too.
To check out the offer at Amazon.com, please click on the image above. By clicking "Read more" below, you can read technical information and specifications. Images taken from this scope are included in the series of information too.
Overview of Telescope resolution:
While small telescopes can show a lot of objects, they may only be seen as colorless dots or smudges. Size does matter in astronomy: bigger is better in many cases.The larger the lens or mirror diameter or aperture, the more light your scope gathers and the higher resolution (ability to see fine detail) it has. Larger scopes also have longer focal lengths, meaning greater magnifications and image sizes are possible with both the eye and cameras. Faint objects like nebulae and galaxies demand large-aperture scopes. Planets need longer focal lengths for higher magnification views and large apertures for high resolution.Nonetheless, here are some recommendations for specific scopes versus specific types of astronomical objects and observing.The sun: a small scope properly equipped with a full-aperture solar filter will provide very good views of the sun under typical daytime seeing (atmospheric steadiness) conditions. A moderate focal length will reveal granulations and sunspot details with your eyepieces. Apertures of 6 inches (150mm) or less and focal lengths of 1000 to 1500mm are good for looking at the closest star.The planets. Here you’ll want a long focal length to take advantage of high magnifications (when the atmosphere is steady enough to use them) to see details in Jupiter’s clouds, Mars’ features, etc. A large aperture is also great for high resolution when using the high magnifications. So the bigger the scope, the better to take advantage of good seeing for planetary viewing. Big scopes will also let you see faint Pluto, planetary satellites and minor planets. The best scopes are at least 5” (125mm) aperture and 1250mm focal length or more.Open (galactic) clusters. Except for the very biggest and brightest clusters (the Pleiades, Hyades, Beehive, Coma Cluster, etc.), you’ll want as large an aperture as you can get and moderate to long focal length as well for the most interesting and field-filling views. The best scopes are at least 5” (125mm) aperture and 1250mm focal length or more.Globular clusters. While pleasing views can be had with smaller apertures, in order to resolve the cores of many of these clusters, you’ll need scopes on the order of 11 inches (280mm) or larger. And correspondingly long focal lengths as well of 1500mm or longer to provide the needed magnification.Nebulae vary enormously in size and brightness. The bright, big ones like the Great Nebula in Orion are actually best seen in relatively small scopes. Larger scopes on this and other objects of its class will reveal details that can’t be seen in smaller scopes. The only sacrifice going to larger scopes is the loss of a wide field of view encompassing the entire nebula. (This is because they will usually have longer focal lengths, resulting in higher magnifications and smaller fields of view with typical eyepieces.) For bright nebulae, choose medium aperture scopes with relatively short focal lengths to capture the entire gas-dust cloud at once. Use apertures of 5-8 inches (125 to 200mm) with focal lengths of 1000mm or less. On the other hand, faint nebulae demand all you can give them in terms of aperture just to capture enough light to see them. Some are also very large – degrees across. Use scopes of at least 8 inches (200mm) and focal lengths of less than a 1000mm for faint, big nebulae. For faint and small nebulae, at least 8 inches and focal lengths of 1000mm or more are recommended.Planetary nebulae: large scopes with long focal lengths are superior. Faint central stars are visually challenging in even the very largest amateur scopes. Use at least 11 inches (280mm) aperture and 2000mm focal length or greater for best results.Galaxies simply demand large apertures and longer focal lengths. With a very few exceptions, they are so far away and so faint that small telescopes will only show them as smudges. If you are a wannabe galaxy hunter, don’t start out with anything less than 8-11 inches (200 to 280mm) to be able to see details in these other Milky Ways.
Technical Data
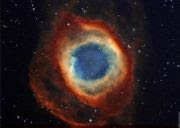
Actual Image Capability:
Dovetail Compatibility:
CG-5 Mount
Aperture:
234.95 mm (9.25 in)
Focal Length:
2350 mm (92.52 in)
Focal Ratio:
10
Finderscope:
6x30
Optical Tube:
Aluminum
Eyepiece 1:
25 mm (0.98 in)
Magnification 1:
94 x
Star Diagonal:
1.25
Optical Coatings:
StarBright / XLT
Secondary Mirror Obstruction:
3.35 in (85.09 mm)
Secondary Mirror Obstruction by Area:
13.1 %
Secondary Mirror Obstruction by Diameter:
36.2 %
Optical Tube Length:
22 in (558.8 mm)
Optical Tube Weight:
20 lbs (9.07 kg)

C9 1/4-A XLT (CG-5) Optical Tube Assembly
Item #91025-XLT






No comments:
Post a Comment